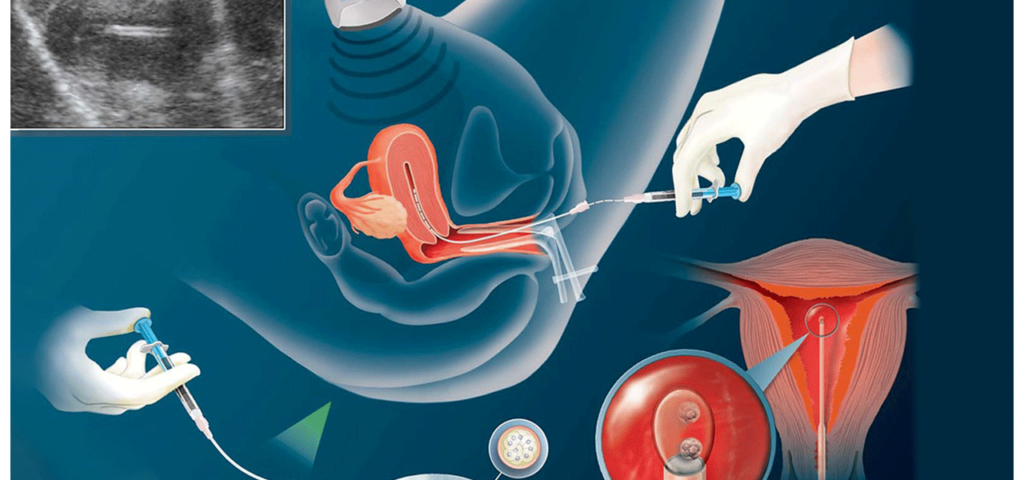
What is IUI – Intrauterine insemination

How a Test Tube Baby is Born?
August 8, 2024Intrauterine insemination (IUI) — a type of artificial insemination — is a procedure for treating infertility.Sperm are washed with gamete media and concentrated are placed directly in wife’s uterus around the time ovary releases one or more eggs to be fertilized.
Why it’s done A couple’s ability to become pregnant depends on many different factors. Intrauterine insemination is used most often in couples who have:
Failure to have natural intercourse: sexual dysfunction, Impotence, vaginismus
- Ovulatory factor infertility. Infertility caused by problems with ovulation, including an absence of ovulation as in PCOD or a reduced number of eggs.
- Endometriosis-related infertility. For infertility related to endometriosis, using medications to obtain a good-quality egg along with performing IUI is often the first treatment approach
- Cervical factor infertility. If your cervical mucus is too thick, it may impede the sperm’s journey. The cervix itself may also prevent sperm from reaching the egg. IUI bypasses your cervix, depositing sperm directly into your uterus and increasing the number of sperm available to meet the awaiting egg.
- Unexplained infertility.IUI is often performed as a first treatment for unexplained infertility along with ovulation-inducing medications.
- Mild male factor infertility (sub fertility) below-average sperm concentration, weak movement (motility) of sperm, or abnormalities in sperm size and shape (morphology). IUI can overcome some of these problems because preparing sperm for the procedure helps separate highly motile, normal sperm from those of lower quality.
- Semen allergy: Rarely, a woman could have an allergy to proteins in her partner’s semen. If your sensitivity is severe, IUI can be effective, since many of the proteins in semen are removed before the sperm is inserted.
- Donor sperm: If Husband is having Azoospermia, women need to use donor sperm to get pregnant; IUI is most commonly used to achieve pregnancy. Frozen donor sperm specimens are obtained from certified labs and thawed before the IUI procedure.
How is IUI done Intrauterine insemination involves careful coordination before the actual procedure:
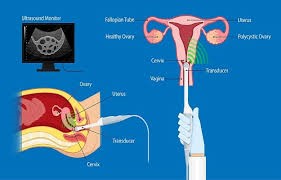
- Ovulation induction and Monitoring for ovulation. Medications for ovulation induction are started on day 2 of periods. Transvaginal ultrasound visualize your ovaries and egg growth can be done. You also may be given an injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) to make you ovulate one or more eggs at the right time.
- Preparing the semen sample.Your partner provides a semen sample at the doctor’s office, the sample will be washed in a way that separates the highly active, normal sperm from lower quality sperm and other elements. The likelihood of achieving pregnancy increases by using a small, highly concentrated sample of healthy sperm.
- Determining optimal timing.Most IUIs are done a day or two after detecting ovulation
What you can expect
The visit for intrauterine insemination takes about 15 to 20 minutes and is usually done in a doctor’s office or clinic. The IUI procedure itself takes just a minute or two and requires no medications or pain relievers.
After the procedure
After insemination, you’ll be asked to lie on your back for a brief period. Once the procedure is over, you can get dressed and go about your normal daily activities. You may experience some light spotting for a day or two after the procedure.
Results
Wait two weeks before taking an at-home pregnancy test.
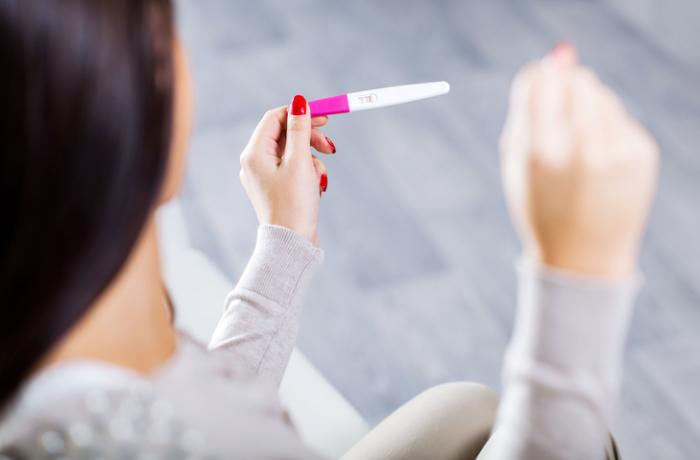

Your doctor may instruct you to return about two weeks after your home kit results for a blood test, which is more sensitive in detecting pregnancy hormones after fertilization.
Success Rate:
20 to 25% with 1 cycle of IUI or 60-70%with 3 or more cycles. If you don’t become pregnant, you might try IUI again before moving on to other fertility treatments. Often, the same therapy is used for three to six months to maximize chances of pregnancy.